Please find the First4Safety Health and Safety Guide for a small business
This article is a simple guide to help small businesses understand the basic requirements of health and safety at work. There are numerous guides available on the internet and from the HSE website also and these will be referenced later in the article.
Firstly before we go into detail it is worth sharing first4safety’s beliefs and mission statement for businesses. At first4safety
‘We believe that all injuries are preventable and our goal for all of them is zero’ We also believe that this is achievable by taking a “Risk based work team approach to Safety management”.
With over 30 years experience working for the top blue chip companies it is absolutely possible to change the culture of an organisation and to reach major behavourial changes in employees attitudes and behaviours that allows you to work in an accident free environment. So lets now look at the steps involved to get your organisation into a position whereby accidents and incidents can be reduced significantly.
Step 1 – Create Health and Safety
Policy
All businesses regardless of size require to have an Effective H&S policy that contributes to business performance
- By minimising the financial losses by avoiding unplanned accidents,
- Supporting quality initiatives aimed at continuous improvement
- Ensuring a systematic approach to identification of risks and by controlling them,
- Recognise that many accidents are a result of failings of management control and not solely the fault of individuals
Step 2 – Organising
 How
How
- The next step is to have in detail a set of defined responsibilities and relationships, which will promote a positive health and safety culture
- by establishing and maintaining control within an organisation ,
- by promoting co-operation between individuals ,
- by ensuring communication of necessary information and
- by securing the competence of employees
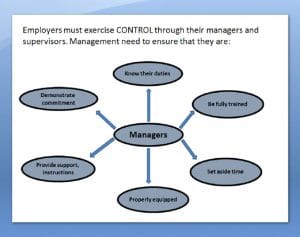
Control
Every business must have in place a Defined clear SET OF PERFORMANCE STANDARDS
– Who is responsible – What are they responsible for
– When should the work be done – What is the expected result
Co-operation
– Actively encourage and support consultation
Communication
– Coming into and flowing within the organisation
– Going out from the organisation
Here are just some of the activities that are required to promote communication – the companies that put resources into good communication processes invariably always have better performance not only safety but also for productivity and quality of service.
- Policy / Vision / Strategy / Values and Beliefs
- Procedures/ Systems / Performance / Lessons Learned
- Visible behaviour: safety tours / chairing meetings / involvement in investigations
- Written communication: policy / statements / performance STD’s / risk control / findings
- Face to face discussions: team meetings / H&S meetings / tool box talks

Competence
- Recruitment and placement procedures – assessment of individuals ability / aptitude / medical
- System to identify training needs – identify training objectives and methods / deliver training / evaluate effectiveness
- Refresher training needs
- Systems and resources to provide Information /Instruction /Training /Supervision
- Arrangements to ensure competent cover
Step 3 – Planning and Implementing
Planning is essential for the implementation of health and safety policies. Adequate control of risks can only be achieved through co-ordinated action by all members of the organisation. Planning must be aimed at
- Controlling risks where are we now? Where do we want to be? How do we get there?
- This requires a Risk Control System / strategy
- Identify key hazards and risks / Risk assessment followed by Risk Control measures
- See full Risk assessment and Method Statements documents

Step 4 – Measuring Performance
Measurement is essential to maintain and improve health and safety performance.
- 1. Active systems which monitor the achievement of plans and the extent of compliance to standards
- Monitor objectives monthly / quarterly
- Performance reviews of managers
- Planned General Inspection’s – Direct behavioural observations
- Inspections by safety manager – Operation of audit system

- Reactive systems which monitor accidents, ill health and incidents, New Green’s accident record is industry best.
You should have effective procedures to capture both sorts of information and more importantly levels of investigations need to be adequate to prevent re-occurrence
- Identify immediate and basic causes
- Identify lack of management controls
- Key lessons learned / prevent recurrences by taking corrective action
Step 5 – Auditing & reviewing performance
Businesses can maintain and improves your ability to manage risks by learning from experience through the use of audits and performance reviews
Your auditing should establishes that
- Appropriate management arrangements are in place
- Adequate risk control systems exist are implemented and consistent with hazard profile
- Appropriate workplace precautions are in place
Process by interviewing individuals / examining documents / visual observation
Reviewing process is aimed to examine the operation and maintenance of the system / the design / development and installation of policy / arrangements. Our reviewing is a continuous process by all levels in the organisation
We hope you enjoyed this initial guide from First4Safety. For further reading we suggest the following links to the official HSE guidance
Managing for health and Safety Hsg65